超过1000篇文献?MemoRAG,下一代 RAG 技术,轻松让AI记住这些海量信息
想象一下,你每天要阅读几十篇文献,整理上千页的笔记,再将这些信息整合到自己的研究中,是不是有点头大?不光是你,很多人都有这样的困扰,尤其是在处理大量信息时。我们总是渴望一种更智能的方式,能帮我们高效地找到、理解并且运用这些知识。而这正是 MemoRAG 的用武之地。
什么是MemoRAG?它到底有什么用?
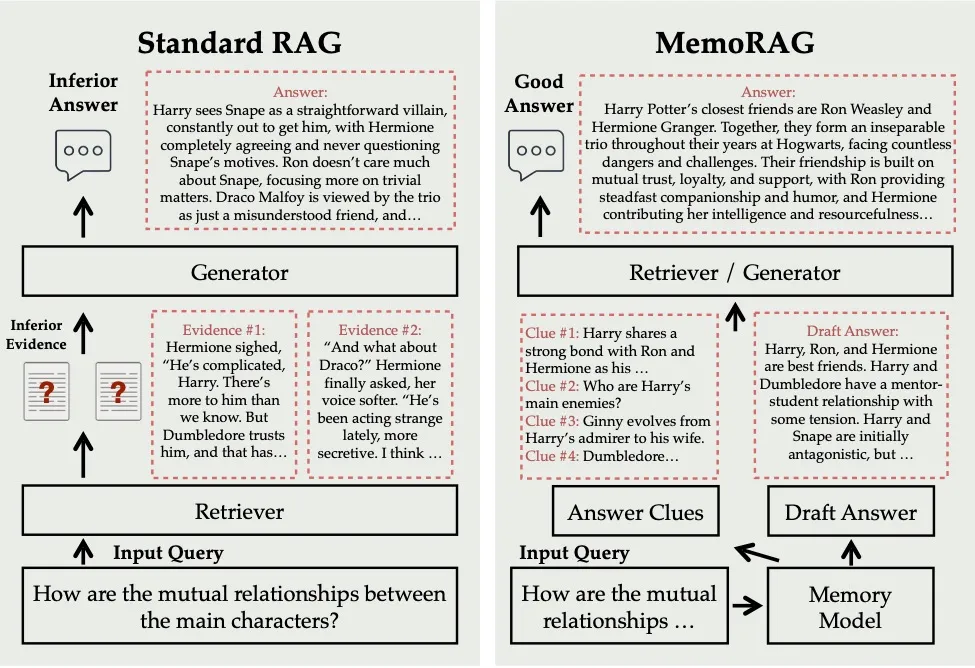
说到 MemoRAG,不得不提一个热门概念:RAG(Retrieval-Augmented Generation)。这个技术让AI模型在生成内容的同时,能够从海量信息中检索出最相关的内容。你可以把它想象成一位超级助理,不仅能回答问题,还能及时查阅相关的文献和资料。
但RAG有一个天然的限制:处理长文档时,它的“记忆力”有限。MemoRAG应运而生,提出了一个新的解决方案:通过引入记忆模块,扩展RAG的知识处理能力。换句话说,它让AI的记忆力更持久,不再只是依赖短期记忆,而是能长时间记住那些长篇大论的内容。
让AI“记住”科研文献
对于研究人员,MemoRAG简直就是量身定制的。当你需要从1000篇文献中提取关键信息时,MemoRAG可以通过建立一个“记忆库”,将那些杂乱无章的内容进行分类、整理和关联。比如,MemoRAG可以自动关联你在不同文献中看到的相似观点,节省你手动翻阅的时间。
企业中的知识管理
企业同样面对海量的信息。MemoRAG可以通过快速检索和记忆关联,帮助公司在短时间内梳理大量信息,做出明智的决策。比如,分析几年的销售数据和客户反馈,传统方式可能耗时数周,而MemoRAG能迅速整合信息,形成清晰的图景。
MemoRAG的“记忆”是如何工作的?
MemoRAG的核心在于记忆模块,它通过创建一个“知识库”,在生成答案时检索相关信息,确保答案的准确性和深度。其设计类似人类大脑,处理新问题时会调用过去的经验来帮助理解。
from memorag import MemoRAG
# Initialize MemoRAG pipeline
pipe = MemoRAG(
mem_model_name_or_path="TommyChien/memorag-qwen2-7b-inst",
ret_model_name_or_path="BAAI/bge-m3",
cache_dir="path_to_model_cache", # Optional: specify local model cache directory
access_token="hugging_face_access_token" # Optional: Hugging Face access token
)
# Load and memorize the context
test_txt = open("harry_potter.txt").read()
pipe.memorize(test_txt, save_dir="cache/harry_potter/", print_stats=True)
# Define the query
query = "How are the mutual relationships between the main characters?"
# Recall clues from memory
clues = pipe.mem_model.recall(query).split("\n")
clues = [q for q in clues if len(q.split()) > 3] # Filter out short or irrelevant clues
print("Clues generated from memory:\n", clues)
# Retrieve relevant passages based on the recalled clues
retrieved_passages = pipe._retrieve(clues)
print("\n======\n".join(retrieved_passages[:3]))
通过这种记忆模块,MemoRAG不仅能生成答案,还能跨越多个文档,处理长篇内容。这对法律、医学、科研等需要处理大量信息的领域尤其有帮助。
MemoRAG的独特优势:打破记忆瓶颈
传统RAG模型通常只能处理几千个字符的文本,MemoRAG通过引入记忆机制打破了这个瓶颈,能处理跨文档的长文本。对于信息密集型的行业,如科研、商业,MemoRAG极大提升了效率,减少了人工操作。
如何在实际应用中使用MemoRAG?
MemoRAG易于使用,可以通过API集成到现有的AI系统中。无论你是科研人员还是企业管理者,都能通过MemoRAG提升工作效率。
from memorag import MemoRAG
# Initialize MemoRAG pipeline
pipe = MemoRAG(
mem_model_name_or_path="TommyChien/memorag-mistral-7b-inst",
ret_model_name_or_path="BAAI/bge-m3",
gen_model_name_or_path="mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2", # Optional: if not specify, use memery model as the generator
cache_dir="path_to_model_cache", # Optional: specify local model cache directory
access_token="hugging_face_access_token", # Optional: Hugging Face access token
beacon_ratio=4
)
context = open("examples/harry_potter.txt").read()
query = "How many times is the Chamber of Secrets opened in the book?"
# Memorize the context and save to cache
pipe.memorize(context, save_dir="cache/harry_potter/", print_stats=True)
# Generate response using the memorized context
res = pipe(context=context, query=query, task_type="memorag", max_new_tokens=256)
print(f"MemoRAG generated answer: \n{res}")
开发者可以使用MemoRAG构建智能文献管理系统,企业可以将其集成到知识管理平台中,帮助员工快速获取所需信息。
未来展望:更智能的AI助手
MemoRAG的出现标志着AI技术在信息处理领域的进步。它不仅解决了长文本处理的问题,还赋予了AI类似人类的“长期记忆”能力。这对信息密集型行业来说,是革命性的进展。未来的AI助手不仅能即时解答问题,还能长期记住你的研究轨迹,为你提供更深度的洞见和决策支持。
开源项目地址:MemoRAG GitHub
MemoRAG为信息处理和知识管理带来了前所未有的可能性。无论是科研、商业还是个人知识管理,它都有广泛的应用前景。如果你正为信息过载烦恼,MemoRAG或许是你所需要的“超级助手”。